| There are two types of glass heat exchangers, coil type and shell and tube type heat exchangers. |
| |
| COIL TYPE HEAT EXCHANGERS |
| |
| Coil type heat exchangers are of all-glass design. There are no internal sealing problems as the coil battery is welded into the jacket making a one piece unit. Coil type heat exchanger are used for condensation of vapours and cooling of liquid. |
| |
| PERFORMANCE DATA |
| The heat transfer coefficients also varies from one size of condenser to another but as a guide, the table below gives as indication of the performance of condenser at atmospheric pressure, using water (inlet temperature 30° C ) as a coolant in the coils and steam condensing in the jackets. The figures do not show the maximum performance of the units but are a general indication of typical working conditions. |
| Jacket sideMedium |
Vapour to be condensed |
Liquid |
Gas |
| Coil side medium |
Cooling water |
Cooling water |
Cooling water |
| Heat transf. coeff. |
– |
– |
– |
|
| |
| PRECAUTIONS TO USE CONDENSER ARE AS FOLLOW |
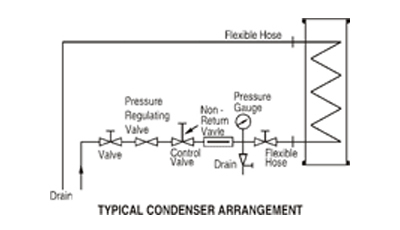 |
| |
|
|
|
When connecting coil-type condensers to the coolant supply, adequate flexible hose should be used to ensure that stresses are not transmitted to the glass. |
|
|
Condenser should never be operated with steam in the coils. They should always be used with an adequate flow of coolant through the coils and care should be taken to ensure that the coolant does not become heated to boiling point. |
|
|
Coolant control valves should always be turned ON and OFF slowly, particularly when air is present in the line. Coolant should be allowed to drain freely to a point as closed as practicable to the heat exchangers. |
|
|
Care should be taken in arranging the coolant supply in order to that water hammer is avoided. A uniform, continuous supply of coolant should be ensured. |
|
|
If a condenser is out of service for any length of time, it is advisable to drain the coils, especially in winter when suitable precautions should be taken to prevent freezing of any water remaining after draining. |
|
|
Brine or other coolants in closed circuit can be used as a coolant provided the suitable precautions against water hammer are taken. |
|
|
Condensers can be mounted in series to provide lager surface area. Generally condensers should be mounted vertically only. |
|
|
The maximum pressure in the coil is 2.7 Bar g the maximum differential pressure |
|
| |
| GLASS CONDENSER |
|
|
| |
| |
COOLANT JACKETTHROUGH FCSA* |
|
|
AREAz
(m²)
|
DN
|
DN1
|
L
|
|
L2
|
TYPE
|
CAP
.LTR.
|
PUT
Kg/h
|
SHELL
(cm²)
|
CAT.
REF. |
| 0.2 |
40 |
16 |
610 |
85 |
100 |
A |
1.0 |
700 |
4.5 |
SHE 1.5/2 |
| 0.3 |
50 |
16 |
610 |
90 |
100 |
A |
1.25 |
1200 |
5 |
SHE 2/3 |
| 0.3 |
80 |
80 |
610 |
90 |
100 |
A |
2 |
1200 |
5 |
SHE 3/3 |
| 0.5 |
100 |
20 |
610 |
120 |
100 |
A |
4 |
2200 |
18 |
SHE 4/5 |
| 0.6 |
100 |
20 |
760 |
120 |
100 |
A |
6 |
2200 |
30 |
SHE 4/6 |
| 1.0 |
150 |
25 |
610 |
150 |
100 |
B |
9 |
2300 |
52 |
SHE 6/10 |
| 1.5 |
150 |
25 |
840 |
150 |
125 |
B |
11 |
2300 |
52 |
SHE 6/15 |
| 2.5 |
225 |
25 |
790 |
180 |
125 |
B |
18 |
3000 |
142 |
SHE 9/25 |
| 2.5 |
300 |
25 |
610 |
250 |
125 |
B |
25 |
2750 |
210 |
SHE 12/25 |
| 4.0 |
300 |
25 |
900 |
250 |
125 |
B |
35 |
4200 |
258 |
SHE 12/40 |
| 4.0 |
400 |
25 |
600 |
350 |
125 |
B |
55 |
4800 |
450 |
SHE 16/40 |
| 5.0 |
400 |
25 |
700 |
350 |
125 |
B |
65 |
5800 |
450 |
SHE 16/50 |
| 6.0 |
450 |
25 |
760 |
325 |
150 |
B & C |
100 |
5800 |
820 |
SHE18/60 |
|
8.0
|
450 |
25 |
900 |
325 |
150 |
B & C |
110 |
6100 |
820 |
SHE 18/80 |
|
| |
| GLASS BOILER |
| Type SHEB 4, SHEB 6 and SHEB 9 glass coil-type boiler are normally mounted in external circulatory loops using a spherical vessel as the main still. They should not be installed in the bottom of a flask or column.
The other types of glass coil-type boilers detailed on this page are again mounted in circulatory loops but as their nominal bore is same at the top and bottom, these units can, under certain circumstances, be installed one above the other to achieve multiples of the basic heat transfer area.
The maximum pressure in the coils is 3.0 barg. The maximum differential pressure across the coils is 3.0 bars. Please refer to the performance data for glass coil-type.
|
| |
DN 150 |
DN 225 |
DN 300 |
| Details of Construction |
Max |
Min |
Max |
Min |
Max |
Min |
| ShellSide |
GlassShell |
2.0 bar.g |
Vacuum |
1.0bar.g |
Vacuum |
0.7bar.g |
Vacuum |
| Steel Shell |
3.5bar.g |
Vacuum |
3.5bar.g |
Vacuum |
3.5bar.g |
Vacuum |
| Tube Side |
Glass Bonnet Single Pass |
2.0 bar.g |
Vacuum |
1.0 bar.g |
Vacuum |
0.7 bar.g |
Vacuum |
| Metal Bonnet Triple Pass |
2.5 bar.g |
Vacuum |
2.5 bar.g |
Vacuum |
2.5 bar.g |
Vacuum |
|
| |
|